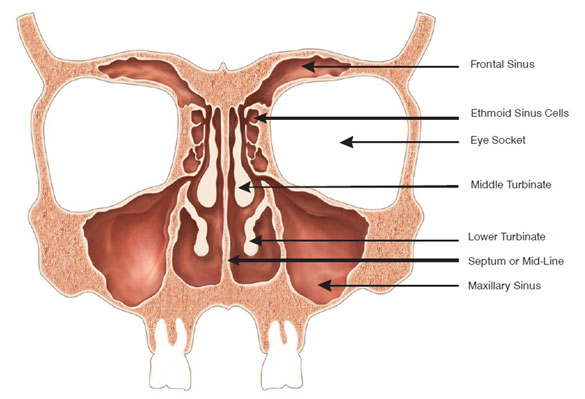
The Sinuses
The sinuses are cavities located in the forehead, cheeks and between the eyes. They have a lining that constantly produces mucus, which is moved out of the sinuses and toward the back of the nose by the action of microscopic hairs (cilia). Dust, allergens, bacteria and fungal spores that are inhaled are trapped in the mucus and usually carried out of the nose by this system, which is very similar to the clearance mechanism of the lungs.
Sinusitis
Sinusitis (properly called Rhinosinusitis) is inflammation of the sinus and nasal lining. It is the result of a combination of impaired mucus clearance, microorganisms (bacteria, fungi, viruses) and inflammation of the sinus lining.
Treatment of Sinusitis
Treatment is aimed at improving mucus clearance, removing microorganisms and reducing inflammation. Medical treatment is usually attempted first, with tablets, sprays and / or nasal washes.
If this is unsuccessful, surgery may be recommended. Surgery is performed to:
- Remove obstructions to mucus clearance
- Remove thick, infected mucus and other material from the sinuses
- Open the sinuses so that after surgery nasal washes and other nasal medications can get into the sinuses
- Improve the airway
Preparing for surgery
Always tell your ENT specialist and anaesthetist about your medical history and be sure to mention
problems such as allergies to medication. Inform your specialists about any medication you might be taking.
This includes any natural medicines such as vitamins and herbal remedies. If there is a family history of blood clotting problems (increased bleeding tendency, easy bruising or deep vein thrombosis) or problems with anaesthetics be certain to mention this as well.
Things to avoid taking at least three weeks before and one week after your surgery:
- Aspirin
- Anti inflammatory medication such as Celebrex or Ibuprofen (Nurofen)
- Vitamin E
- Fish oil
- Garlic, ginger, ginseng and any other herbal remedies (there are more than 40 different herbs which have effects on blood clotting)
These substances can cause excessive bleeding and should be avoided around the time of surgery. Excess bleeding during the surgery makes surgery more difficult and can result in the procedure being stopped before it is completed. Bleeding after surgery can occasionally require treatment with nasal packing or more surgery.
Warfarin, Clopidigrel (Plavix) or aspirin taken for heart or stroke problems will also need to be stopped before surgery, however this should be discussed with both your ENT surgeon and your GP or cardiologist. Other short acting medications may be needed.
You should stop smoking as soon as possible. It is advisable to use this opportunity to quit smoking altogether.
Please remember to take your CT scans to the hospital – your surgery will not proceed without them.
Medication Sprays










